




SPLAT OFM releases pheromones that interrupt the meeting of male and female grapholite insects. Grapholite insects are also known as oriental moths. When distributed throughout the plantation, the product releases pheromone trails into the wind. These trails attract male grapholite moths, who follow the synthetic pheromone to its source rather than authentic pheromones to female moths.
Our products are capable of controlling oriental moth populations by interrupting the the moths reproductive cycle in the field. This protects injuries to fruit from caterpillars and economic damage created by loss of product.
Pheromones are compounds produced by insects and other animals that serve for communication between members of the same species. Several species utilize pheromones to communicate with each other to transmit information regarding food, danger, more efficient trails, or a desire to mate.
SPLAT OFM is a formulation that involves a synthetic sexual pheromone similar to the one released by the female Grapholita molesta to attract the male for copulation. To learn more about how and when to use this product, consult one of our technicians.
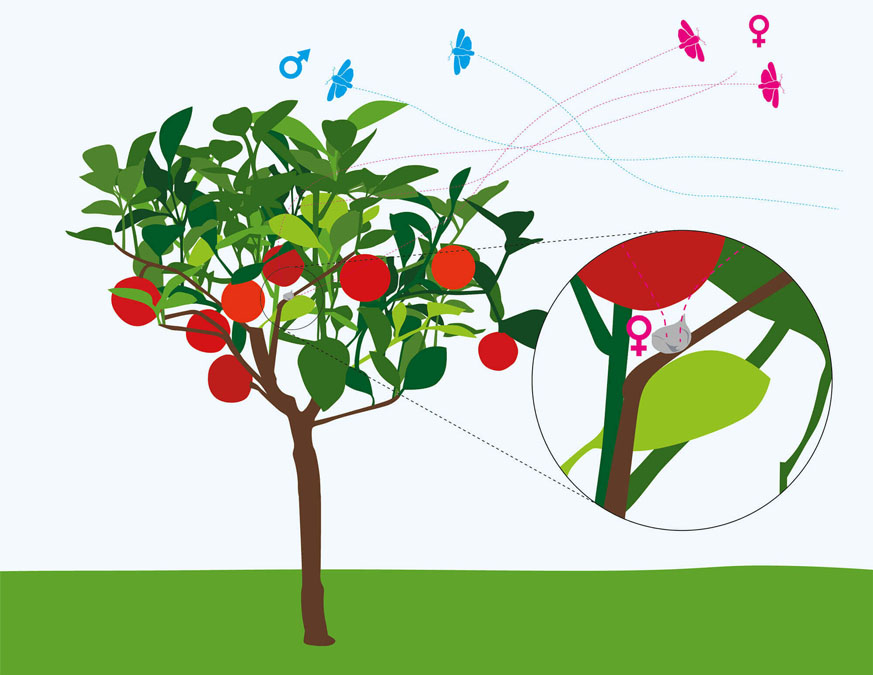
The synthetic sex pheromone is similar to what the female releases to attract the male to copulation, creating trails that confuse him and prevent reproduction and the appearance of the caterpillar

Peach, apple, pear, and quince are some of the crops protected grapholite attacks by SPLAT OFM
SPLAT OFM is a biological product designed to control populations of Grapholita molesta (a type of moth) in peach, apple, pear, nectarine, loquat, plum, and quince orchards as well as any other fruit sites where the target insect is present.
SPLAT OFM is indicated for use in IPM (Integrated Pest Management) as a control tool to be combined with other biological or conventional products. This product allows users to control pests without leaving residue in fruits. Farmers benefit from this product in production programs with restrictions on pesticide molecules in fruits.
PRODUCT description
INDICATION FOR USE
BENEFITS
TARGET INSECT
Apply SPLAT OFM starting when you see Grapholita molesta in flight for the first time after the winter diapause. The product must be dispensed with a hand-held applicator or an appropriate mechanical device.
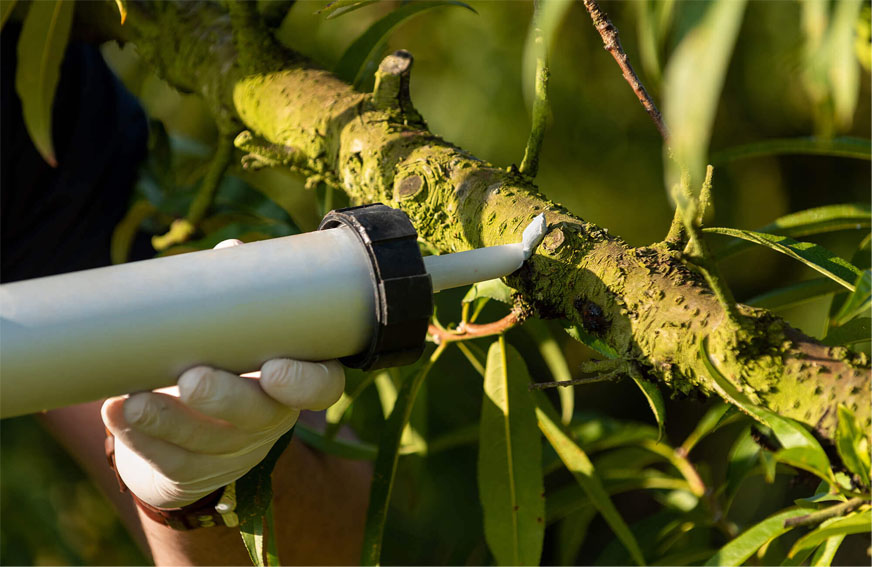

SPLAT OFM being applied to a peach tree branch
SPLAT OFM is an effective product that acts on grapholite before the insect oviposition. Action taken before oviposition helps to reduce potential damage. Its differentiated mode of action helps in IPM systems (Integral Pest Management) without leaving residues inside fruits. SPLAT OFM also reduces the resistance of insects to insecticides. The product does not affect natural predators of the pest nor pollinators which allows for beneficial effects of both parties to be carried out.
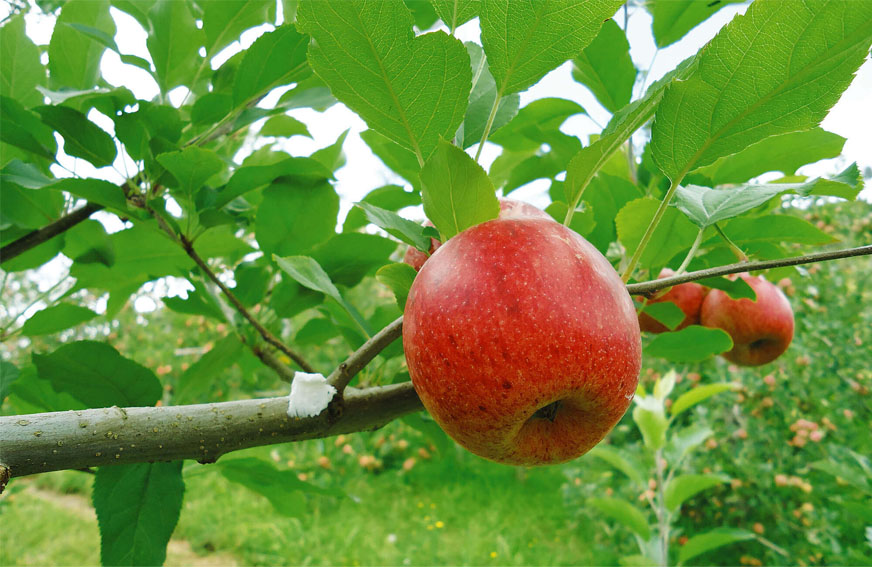

SPLAT OFM`s mode of action does not leave residues on fruits. It also does not affect pollinators or grapholite`s natural predators.
SPLAT OFM uses significantly less water than conventional control methods do. The product reduces the number of insects and crop damage, while optimizing the use of insecticides and conserving natural enemies of the pest.
PRODUCT description
INDICATION FOR USE
HOW TO APPLY
BENEFITS
Grapholita molesta is a moth that originated in northwest China then spread to Japan and Australia. Grapholita molesta traveled from the east to central Europe, then to the east coast of the United States, and made its way to Brazil by the beginning of the 20th century. Today its presence is confirmed on all continents and occupies dozens of countries. This moth’s quick spread is attributed to its ability to fly. Fruits and plants that the moth uses as hosts were sent to different countries internationally and also contributed to the moth’s spread. In Brazil, Grapholita molesta is most prominent in São Paulo, Minas Gerais, Paraná, Santa Catarina, and Rio Grande do Sul. This moth causes the most significant damage and crop loss to apple fields, but also preys on peaches, nectarines, plums, cherries, pears, asian pears. And quince. Some of the damage done by G. molesta on buds and fruits can appear similar to that of Anarsia. G. molesta females lay from 50 to 200 eggs individually on the underside of leaves. Each egg is around 0.7 mm in diameter, white with a gradual change to yellow, and variable in shape, ranging from convex to round. Larva that emerges from these eggs are about 12 mm long and red with a brown head. Pupas of this species are reddish-brown. This moth can cause two types of damage, old injury and new injury. Old injury refers to damage caused by larvae that have abandoned branches and feed on new fruit at the beginning of the season. New injury refers to damage caused when the moth enters fruit through the stem when fruit is fully grown.
